For most Americans, the filing deadline for the 2024 tax year is April 15, 2025.¹ Since this deadline has a way of sneaking up on us, we put together a tax documents checklist to cover tax fundamentals and the information you need to file early and easily.
Complete tax preparation checklist
The tax deadline can feel like it’s looming, especially if you’re not sure how to do your taxes. The good news is, you have plenty of time to prepare.
To get a jump-start on tax prep long before tax day, use our comprehensive checklist to make sure you have the documents you need to file before tax time rolls around.
Personal information: what do I need to file my taxes?
First, make sure you know what tax bracket you’re in. Then, prepare your personal information,² including:
- Social Security number (SSN) or tax ID number (ITIN)
- Your current address
- Bank account routing and account number for your refund or to pay your balance
- Your adjusted gross income (AGI) and your refund amount from your last tax return
- If you e-filed last year, your self-select PIN
- If married, your spouse’s full name and social security number or tax ID number
- If married, your spouse’s date of birth

Dependent(s) information
If you have any dependents, you must prove that they are a qualifying child, sibling, parent, or other relative. To do this, you’ll need to have these documents ready to go:³
- Proof of citizenship (they must be a U.S. citizen, U.S. resident alien, U.S. national, or a resident of Canada or Mexico)
- Dependent’s date of birth
- Social Security numbers or tax ID numbers
- Child care expense records, which should include the provider’s name, address, and tax ID number
- Form 8332 if the child’s custodial parent has given you the right to claim them as a dependent⁴
- Sources of income if dependents are working
- Income for any other adults in your home
- Proof of custody arrangement: In split custody cases, the IRS uses tiebreaker rules to choose which parent or guardian gets to claim the child (or children) as a dependent. To prove that you have the right to claim a child, you will probably need to bring documents that outline your custody arrangement or child support agreement.⁵
Income tax documents
Here’s an overview of the income documents you should receive depending on how you earned money during the last tax year and which forms you need to file.
Employed full-time
Every year, your employer should send you a W-2 form if you are a non-contractor employee. The form details your earnings and taxes withheld from your paycheck throughout the tax year.
What you’ll file: Form 1040, using the information from your W-2.
Unemployed
If you were unemployed and received unemployment benefits during the tax year, you should receive a Form 1099-G, which shows the amount of unemployment income you received from the government.⁶
What you’ll file: Form 1040, using the information from your Form 1099-G.
Self-employed
You may receive either a Form 1099-NEC from any company that hires you as a freelancer or independent contractor. Or a Form 1099-K from any third-party payment platform you use to collect payment from customers.⁷
What you’ll file:⁸
- Form 1040, including the information from your 1099s, and include records of income not reported on the 1099s
- Schedule ES (included on your 1040) to report any estimated tax payments made
- Schedule SE (included on your 1040) to pay any self-employment taxes you owe
- Form 8829 to report and deduct applicable expenses that resulted from the business use of your home
- Schedules K-1 on Form 1065 for business partnerships, business owners, or co-owners to report any losses or income
Rental income
If you own rental properties, you’ll need to report any rental income you received throughout the tax year for each rental property. You won’t receive any form, so you’ll need to keep your records organized throughout the year or start collecting them now.⁹
What you’ll file:⁸
- Schedule E (on your Form 1040) to report any income or loss from rental real estate
- Schedule ES (on your Form 1040) to report any estimated tax payments made

Retirement or social security income
Your financial institution will send your Form 1099-R if you withdrew funds from a retirement account like a pension, annuity, or IRA.⁸ If you receive social security benefits, you’ll receive an SSA-1099, and for any Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) benefits, you’ll receive the Form RRB-1099.¹⁰
What you’ll file:⁸
- Form 1040 or 1040-SR (a simpler version of the 1040, for seniors) to report the income from your 1099s
- Form 5329 to report any additional taxes on qualified plans
- Form 8606 for nondeductible IRAs
Savings & investments or dividends
Your bank or brokerage firm will send you Form 1099-B if you sold stocks (including cryptocurrency), bonds, or any other type of security, and a Form 1099-S documenting the income and acquisition dates of any real estate sales. If you earned dividends, you’ll receive Form 1099-DIV, and if you earned any interest, you’ll receive Form 1099-INT.
If you have a health savings account (HSA) or Medicare Advantage medical savings account (MA MSA), your HSA or MSA provider should send you a Form 1099-SA. And if your insurance company pays any long-term care benefits, you should receive a Form 1099-LTC.
What you’ll file:⁸
- Form 1040 to report everything from your 1099s
- Schedule ES (on your Form 1040) to report any estimated tax payments made
- Form 8949 to reconcile the amounts from your 1099-B or 1099-S
- Schedule D (on your Form 1040) for capital gains or losses
Ultimately, the forms you receive and file may change based on your unique tax situation – consult a certified tax preparer if you need advice.
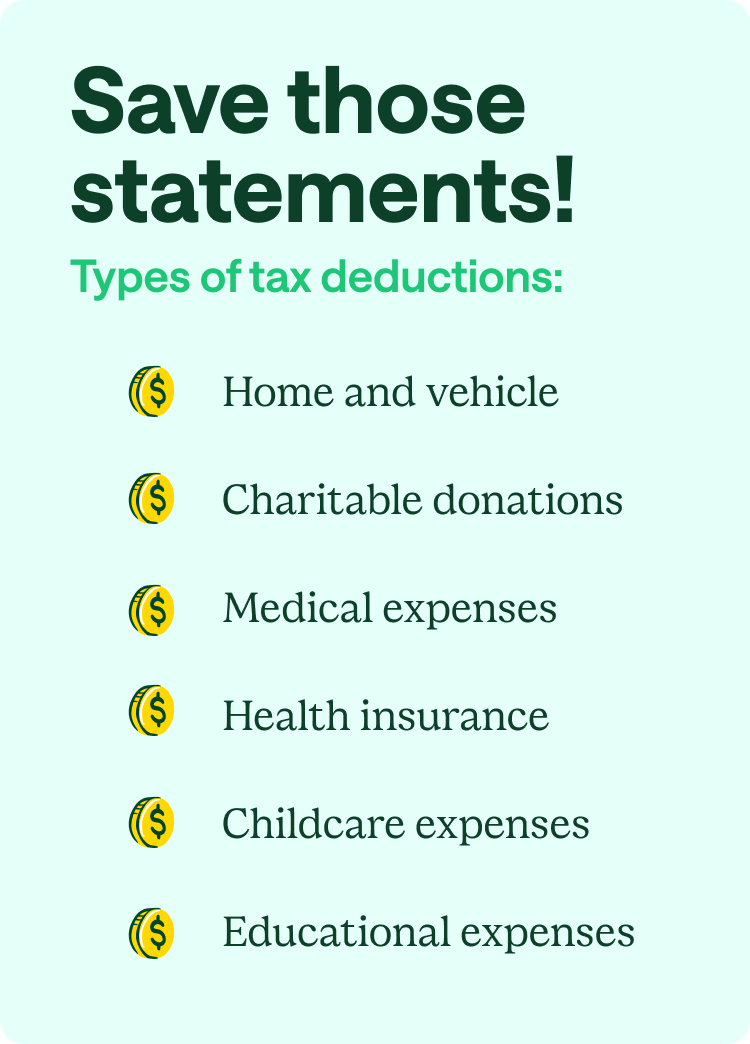
Types of tax deductions
To qualify for an income adjustment, which reduces your adjusted gross income (AGI) based on certain tax deductions, you’ll need to provide documentation as proof of certain expenses.
Common deductions include payments for student loan interest, tuition, classroom supplies (for teachers), IRA contributions, alimony, self-employed pension plans, energy-efficient home equipment, and contributions to Medical Savings Accounts (MSA) or Health Savings Accounts (HSA).
If you don’t qualify to lower the amount you’re taxed, chances are you can still claim tax credits that reduce the amount you owe. You will need to take the itemized deduction to claim most of these write-offs, so hold onto your receipts until after you file.
Below are some of the top tax deductions to claim in 2024 if you qualify – not all of these will apply to you.
Home ownership
You can use Form 1098 to deduct mortgage interest, along with receipts to claim residential energy credits and records showing that you used a home equity loan to make improvements to your property to claim the home equity loan interest deduction.¹¹
Homeowners and renters who work from home can submit statements, receipts, and records to deduct insurance, utilities, maintenance, repairs, rent, and more.¹²
Charitable donations
You can submit receipts, bank statements, mileage statements, or written acknowledgments to prove that you donated (cash or non-cash) to places of worship, nonprofits, schools, foundations, or other charitable organizations.
You can calculate and report those charitable donations using Schedule A (Form 1040).¹³
Medical expenses
The IRS lists various medical and dental expenses you may be able to deduct, depending on what you paid for throughout the year. You can submit receipts for medical expenses, doctor’s visits, and medicine to claim this deduction on Schedule A (Form 1040).¹⁴
Health insurance
If you have insurance through the Affordable Care Act insurance marketplace, you may qualify for the premium tax credit. You should receive Form 1095-A, which you’ll use to complete Form 8962 with your return.¹⁵
Childcare expenses
If you paid someone to care for your children (under age 13) throughout the year so that you or your spouse could work (or look for work), you can submit receipts or invoices to claim the Child and Dependent Care Credit.
If you do quality for the credit, complete the Form 2441 and attach it to your Form 1040.¹⁶
Educational expenses
Certain educational expenses are eligible for tax deductions. Generally, qualified expenses cover tuition, student loan interest, fees, and required enrollment costs at eligible schools.
However, expenses like room and board, insurance, medical fees, transportation, personal costs, and non-credit courses (unless degree-related) don’t qualify. Student activity fees are eligible only if required for enrollment. And you’ll need to show any records of scholarships or fellowships you received.¹⁷
You should receive Form 1098-T from educational institutions for tuition and Form 1098-E for any student loan interest paid. You will use these to fill out your Form 8863 and submit it with your Form 1040.¹⁸
K-12 educator expenses
If you’re an educator in grades K-12 and spent money on any classroom materials, professional development courses, books, or any other supplies for the classroom, submit your receipts to claim the Educator Expense Deduction on Form 1040 with Schedule 1 attached.¹⁹
State and local taxes
You may be eligible to deduct certain state and local taxes from your federal income, including:
- Local income tax: Tax on income earned within a specific city or locality, paid to local jurisdictions.
- State income tax: Tax on income earned within a state, applicable to individuals and businesses.
- Sales tax: Tax on purchases of goods and services, calculated as a percentage of the sale price.
Keep records of any major purchases, as well as invoices for any vehicle sales tax paid. You’ll file Schedule A on your Form 1040.²⁰
Retirement & other savings
You might be able to claim a deduction if you contributed to a traditional IRA (single or joint), a traditional 401(k), an MSA, or an HSA throughout the tax year.
You should receive Form 5498 showing any IRA contributions and retirement plan transactions — then complete Form 8880 and submit it with your Form 1040.²¹
Federally declared disaster
You might be able to claim the Casualty Loss Deduction if you lived, worked, or had property in a federally declared disaster area. Submit evidence of insurance claims, photographs, records to prove losses and building repairs, or damage reports using Form 4684 and attach it to your Form 1040.⁸

File taxes with confidence
With tax season approaching, having the right documents can make the filing process smoother and less stressful.
Whether you choose to file independently, use tax software, or hire a professional, taking time now to gather essential forms and documentation will help you file accurately, claim deductions, and avoid issues.
Consulting a tax professional can offer personalized insights and maximize your deductions if you have a complex financial situation.
Got all your documents ready? Here’s how to file taxes online.
FAQs
What documents do I need to include with my tax return?
You’ll need income-related documents like W-2s or 1099s, receipts for deductions, and any other forms that report taxable income or eligible tax credits.
What are the five main categories of documents that you need to file your taxes?
The main categories are personal information, dependent(s) documentation, income and investments statements, tax deduction and tax credit documentation, and records of any tax payments you’ve already made.
What’s the most common tax document?
The most common tax document is the W-2, which reports wages and taxes withheld for employees.
What order should my tax documents be in?
Tax documents should be organized by type, starting with personal information and income forms (W-2, 1099s), followed by deduction and credit forms and any supporting documents or receipts.