A credit score is a three-digit number that tells lenders whether you’re likely to pay back loans on time or not. FICO® scores are the most widely used credit scores, which range from 300 to 850.¹ The higher the score, the more reliable you appear to lenders.

While a credit score is a single numbered score, every person has multiple credit scores issued by different credit bureaus and scoring models.
Multiple factors determine your credit score, including your payment history, credit utilization, credit history length, credit mix, and new credit applications. With a credit score in the good to excellent range (typically 670 or higher), you increase your chances of being approved for loans or credit cards, and with better terms and rates.
How credit scores work
Think of your credit score like a financial report card that lenders use to assess the risk of lending you money. When you apply for a credit card, loan, or mortgage, lenders review your credit score to gauge the likelihood that you’ll repay them as agreed.
A higher credit score shows responsible financial behavior, which is more attractive to lenders. They’re more likely to offer you lines of credit, often at lower interest rates, which can save you money over time. Conversely, a lower credit score may result in higher interest rates or credit application rejections.
Credit scores typically fall within a range, and what is considered high or low can vary depending on the credit scoring model used. The most common scoring models come from the three major credit reporting agencies:
- Equifax
- Experian
- TransUnion
As mentioned earlier, the FICO credit score model is one of the most common. It uses a credit score range between 300 and 850, where higher numbers indicate less credit risk. Here’s a breakdown of the FICO scoring model:
| Credit score² | Rating |
|---|---|
| 800-850 | Excellent |
| 740-799 | Very good |
| 670-739 | Good |
| 580-669 | Fair |
| 300-579 | Poor |
How your credit score is calculated
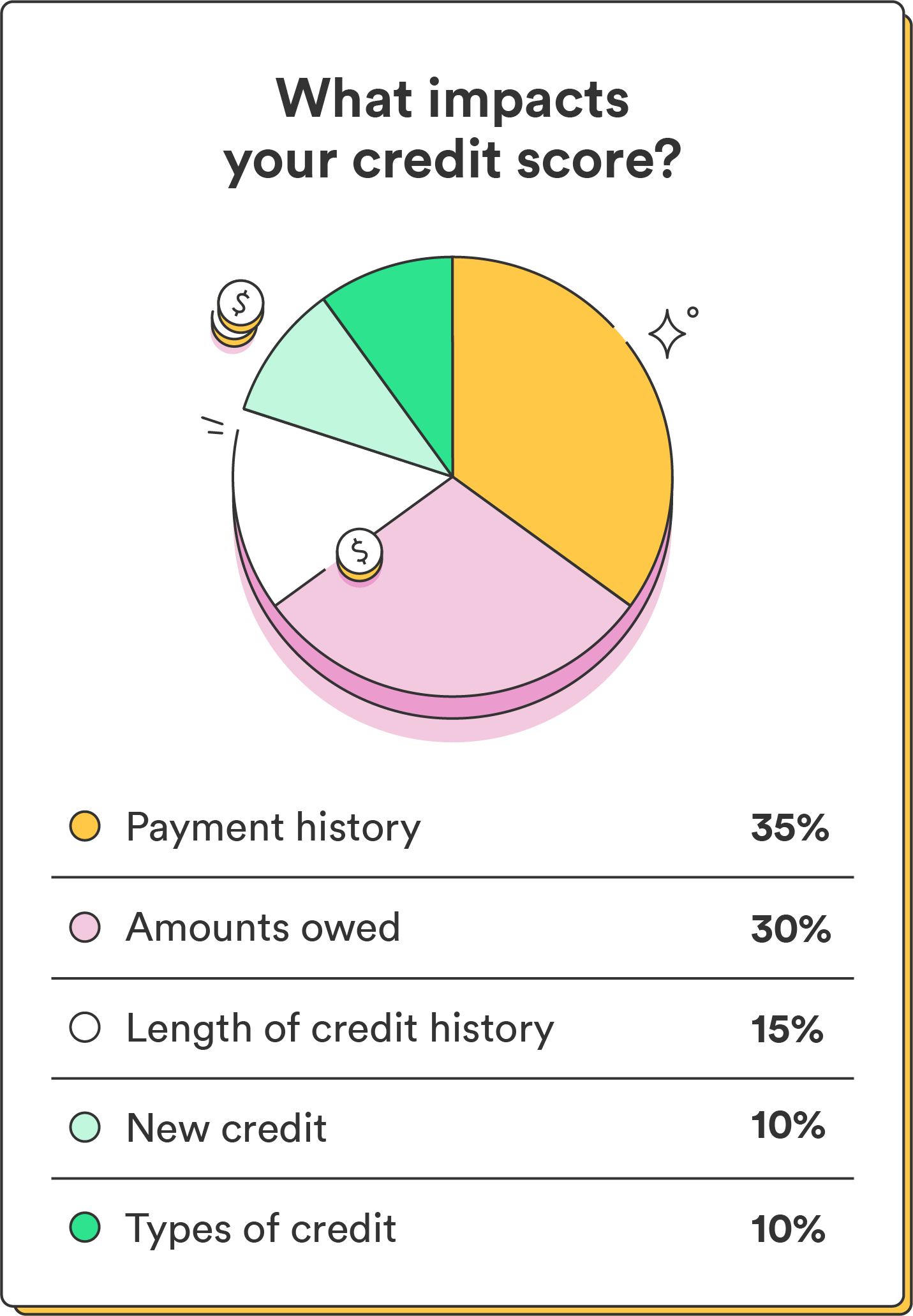
The three main credit bureaus, Equifax®, Experian®, and TransUnion®, base your credit score on the information in your credit reports. In general, five main factors influence your credit score, as seen in the FICO categories below:
- Payment history (35%): This is your track record of making on-time payments on time or any missed payments. The most critical factor in your credit scores is paying your bills on time, every time.
- Credit utilization (30%): This is the amount of credit you use compared to your total available credit limit. Lenders like to see low credit utilization ratios – if you max out all your cards, they probably won’t want to pile on more credit.
- Length of credit history (15%): This is how long your credit accounts have been open. Closing your oldest credit account) could ding your credit in some cases since it reduces your average age of accounts.
- Types of credit used (10%): This is the mix of credit accounts you have, including credit cards, loans, and mortgages.
- New credit applications (10%): This includes credit applications, which can temporarily lower your score. Lenders might assume you’re financially unpredictable if you’ve just opened many new accounts.
When you use any type of credit, your lender, bank, or other financial institution tracks your activity and reports it to the credit bureaus mentioned above. Then, they use a scoring model (like FICO) to calculate your score. VantageScore® is another widely used scoring model.
How to check your score
There are a few different ways to check your credit score:
- Check your credit card or loan statement: You may be able to find your credit score on your statement or by logging in online or on your mobile device if you have an open credit account.
- Use a credit monitoring service: Various credit monitoring services are available, including Credit Sesame® or Experian’s free credit monitoring. These services give you access to your credit score and provide ongoing updates to your credit activity.
- Go through the three major credit bureaus: You can get your credit score directly from the websites of the three major credit bureaus. While some may offer to view your credit score for free, you can also purchase a more detailed credit report for a fee.
You can also go to AnnualCreditReport.com for one free copy of your credit reports from all three main credit bureaus. While these reports won’t contain your credit score, they can still provide a comprehensive overview of your current credit and financial standing. You can also track your FICO score in the Chime app for free.
Why you may have different credit scores
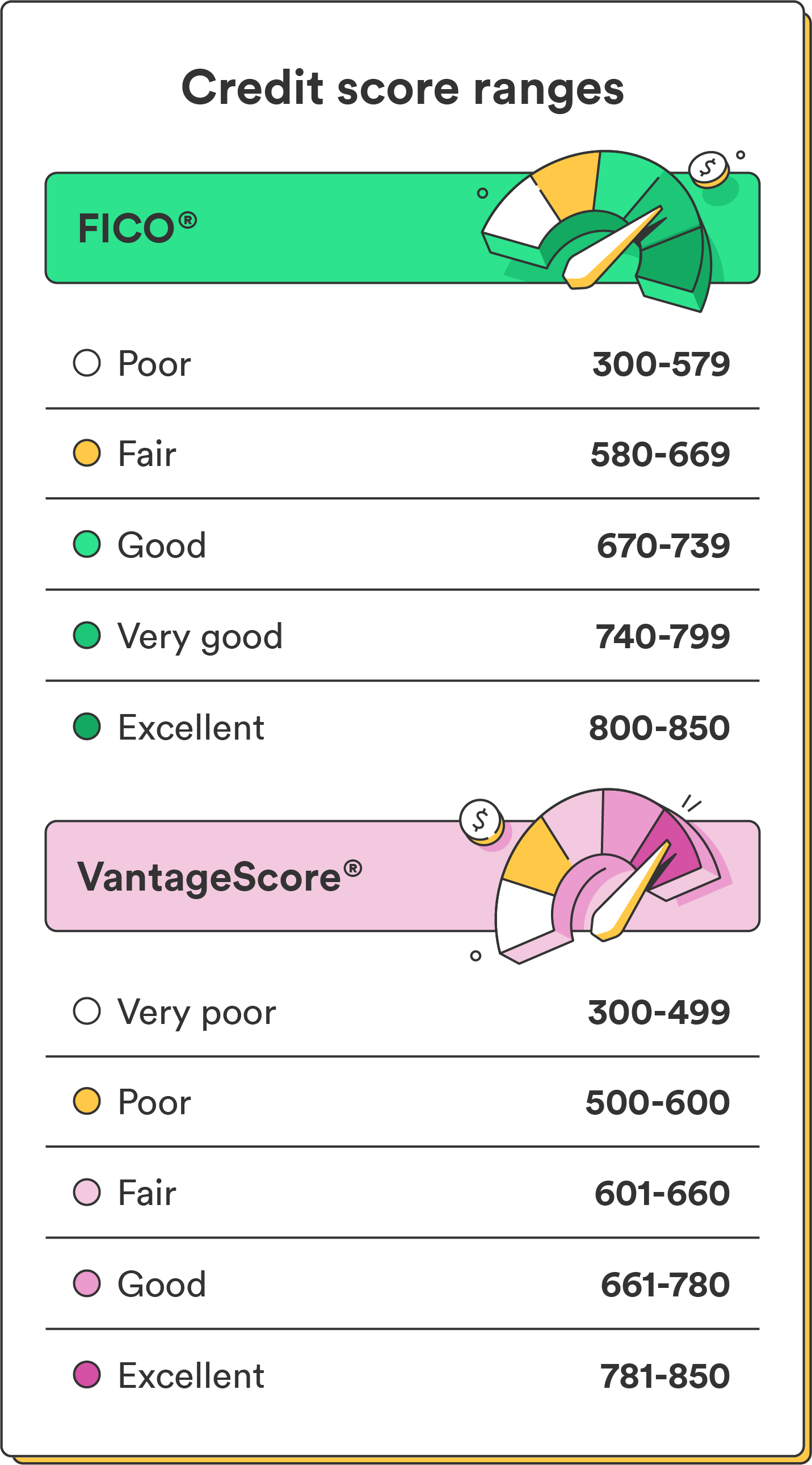
Various scoring models, like FICO and VantageScore, have unique algorithms, credit score ranges, and factor weightings. As a result, you may get a different evaluation from each model, leading to credit score variations.
There are a few other reasons you may have different credit scores:
- Timing: Creditors report data to the bureaus at different times, so your credit report may sometimes reflect different information.
- Industry-specific scores: Lenders may use industry-specific credit scores tailored to their type of lending, like auto or mortgage scores.
- Only reporting to one or two credit bureaus: Not all lenders or credit issuers have to report your activity to all three credit bureaus. The score you get from one bureau could be missing information that could impact your score.
For these reasons, it’s normal for your credit scores to vary slightly from each bureau.
| FICO credit score ranges² | VantageScore credit score ranges² |
|---|---|
| 800–850 (Excellent) | 781–850 (Excellent) |
| 740–799 (Very good) | 661–780 (Good) |
| 670–739 (Good) | 601–660 (Fair) |
| 580–669 (Fair) | 500–600 (Poor) |
| 300–579 (Poor) | 300–499 (Very poor) |
How to improve your credit score
Your credit habits can make or break your credit score. While you can’t always control how quickly you build or improve your credit score, following the tips below will help improve your score over time:
- Pay bills on time: Consistently making on-time payments is one of the most significant factors in improving your credit score.
- Keep credit utilization low: Aim to lower your credit card balances to below 30% of your credit limits. Lower credit utilization can positively impact your score.
- Keep old accounts open: The length of your credit history matters. Keep older, well-managed accounts open to demonstrate a longer credit history.
- Diversify your credit mix: A mix of credit types, like credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can positively influence your score.
- Avoid opening too many new accounts: Multiple credit inquiries at once can lower your score. Avoid applying for multiple new credit lines within a short period.
- Regularly check credit reports for errors: Monitor your credit reports for inaccuracies or errors and call the credit bureaus to correct them.
In addition to the healthy credit habits above, remember to be patient – improving your credit score takes time. With dedication and consistency, your credit score should gradually improve.
Start building your credit score now
Good credit can help you go far in life, and working to improve your credit can help you land better rates and terms in the future. Remember that your credit-building journey is a marathon, not a sprint. While it may take some time, your responsible credit use will eventually pay off.
Learn more about what a good credit score is in your 20s and beyond.
FAQs about credit scores
How often should I check my credit score?
Check your credit score at least once a year from each of the three major credit bureaus using a site like annualcreditreport.com. However, if you’re planning a major financial decision, like applying for a loan, you may check it more frequently, such as monthly.
Can checking my own credit score hurt it?
No, checking your own credit score, often called a “soft inquiry” or “soft pull,” doesn’t harm your credit. It’s a routine part of credit monitoring and does not impact your credit score.
How long does it take to improve a credit score?
The time it takes to improve a credit score varies widely based on your circumstances. Generally, you can see some improvement within a few months by making on-time payments and reducing credit card balances. Significant changes could take several years, especially if you have negative marks.
Does closing old accounts affect my credit score?
Closing old credit accounts can potentially harm your credit score since it could shorten your credit history and reduce your overall available credit. Closing an account can impact your credit utilization ratio. If the closed account had a positive payment history, its positive impact on your credit score may slowly diminish.
How long does negative information stay on my credit report?
Most negative information, like late payments, collections, and bankruptcies, can remain on your credit report for seven to 10 years, depending on the type of negative mark. However, their impact on your credit score lessens over time, and you can work on improving your credit during this period.

 Log in
Log in